 Medicaid is the single largest healthcare provider in the United States. While Medicaid programs are run by the states, they are also subject to federal rules and regulations. In 2010, President Obama expanded Medicaid coverage for millions of Americans through the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA created the opportunity for states to expand Medicaid to cover nearly all low-income US citizens under age 65, and adults with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty line. Today, 78.5 million Americans rely on Medicaid for healthcare coverage. While most states include emergency dental care benefits for adults, less than half provide comprehensive dental care.
Medicaid is the single largest healthcare provider in the United States. While Medicaid programs are run by the states, they are also subject to federal rules and regulations. In 2010, President Obama expanded Medicaid coverage for millions of Americans through the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA created the opportunity for states to expand Medicaid to cover nearly all low-income US citizens under age 65, and adults with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty line. Today, 78.5 million Americans rely on Medicaid for healthcare coverage. While most states include emergency dental care benefits for adults, less than half provide comprehensive dental care.
The ACA requires that any health insurance policy purchased for children under the age of 19 must include dental benefits. At a minimum, plans are required to cover dental services relating to maintaining dental health, restoring teeth and relieving pain and infections.
Medicaid plans for adults do not require dental benefits and are considered an “option” for states to cover.
- 13 states offer emergency care for Medicaid recipients who require immediate relief of pain or acute infection.
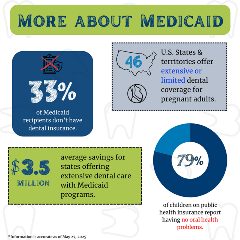
- Four states offer no dental coverage for adults.
- 15 states offer limited plans for adults, typically covering some or all preventative care, fillings and extractions.
- 19 states offer full dental benefits for adults.
While Medicare provides critical healthcare coverage for seniors and individuals with certain disabilities, it rarely covers the cost of routine dental care, including cleanings, fillings and extractions. Medicare Advantage is a federal program that contracts with private insurers to offer additional benefits that Original Medicare does not cover, like dental and vision benefits.